Developments in Preservation of Traditional Dairy Products. The short shelf life of the traditional dairy products is the major limitation inorganized marketing of these products.
The conventional preservation techniques such as sterilization, freezing, etc. cannot be used for traditional dairy products due to their adverse effects on sensory and textural quality. This calls for application of newer concepts of food preservation such as hurdle technology, bio-preservation, modified atmospheric storage, etc.
Hurdle technology- Use for Preservation of Traditional Dairy Products
The microbial stability and safety of most traditional foods is based on a combination of several preservation factors, called hurdles, which microorganisms present in food are unable to overcome.
These hurdles include water activity, pH, heat treatment, sugar, salt, redox potential, preservatives, etc. Hurdle technology involves optimization of 3 or more hurdles so that shelf life and the microbial safety is extended without adversely affecting overall quality of the product.
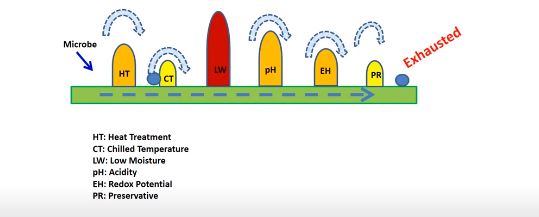
The advantages of hurdle technology
(i) The sensory and nutritional characteristics of food remain close to fresh/natural ones
(ii) Less energy consumption
(iii) Auto sterilization of foods is observed during storage
(iv) Less susceptible to non-enzymatic browning and lipid oxidation.
The first ever-successful application of hurdle technology in India was made in authors laboratory for preservation of ready-to-eat Paneer curry by Rao and Patil in 1999. It involved optimization of water activity, pH, extent of heat treatment and level of preservatives to obtain shelf-stable product. The product has a shelf life of one month.
Bio-preservation
Another emerging technology for preservation of perishable foods is bio-preservation. It refers to extended shelf life and enhanced safety of foods using their natural or controlled microflora and/or their antimicrobial products.
The lactic acid bacteria synthesize variety of inhibitory substances including bacteriocins or bacteriocidal proteins.
Currently large-scale attempts on application of natural antimicrobials for food preservation are being carried out. Nisin was the first recognized antimicrobial substance produced by lactic streptococci that has realized commercial application in food preservation.
Use of nisin in extension of shelf life of Khoa, Lassi, and sterilized Kheer has been reported . Many other bacteriocins produced by Lactobacillus spp. such as lactocin 27, helveticin J, Lactocidin, Plantaricin A & B, Sakacin ñ A, brevicin, Pediocin PA-I, pediocin AcH, Pediocin-A, Leucocin demonstrate broad range of antagonistic activity against many spoilage organisms.
These bacteriocins need to be exploited for preservation of traditional dairy products. They will be particularly effective when used in combination with hurdle technology.

Osmotic dehydration
The concentration of food products by means of product immersion in a hypertonic solution is known as osmotic dehydration. This process has received considerable attention in recent years because of potential industrial application.
Compared to air drying or freeze drying, osmotic dehydration is easier as less energy consuming because of removal of water occurs without a phase change. As the food product dehydrated by osmosis is not subjected
to high temperatures for extended periods, the heat damage is also minimized.
The technology has great potential in near future for dehydration of indigenous dairy products. Successful attempts have been made at laboratorys to dehydrate rasogolla and paneer using this technology.
Individual quick freezing (IQF) process
IQF process is another technology, which can be used for extending the shelf life of the traditional dairy products.
IQF is a continuous process in which the product moving on the belt is exposed to a blast of extremely cold air freezing it in a matter of seconds.
This serves two purposes i.e. there is no time for the product to deteriorate and because it is frozen instantly the pieces do not stick to each other. Thus there are no clumps or blocks and one can take out even one individual piece without having to defrost or cut the frozen product.
The great advantage of IQF is that the product reverts practically to its original fresh state when used for consumption. The technology will be useful for preservation of paneer, rasogulla, gulabjamun, etc.
Intermediate moisture products
Reducing water activity of the food product to the intermediate moisture range is a well-known method of food preservation. This technique has recently been applied successfully to preserve paneer cubes. The intermediate moisture paneer has a shelf life of 4 months at room temperature and can be reconstituted within five minutes.
Conclusion
In conclusion we can see that Innovative technique has great scope in preservation of traditional dairy products, and industry can use this methods to preserve the foods and can use this techniques for export the product with high quality standards and make impact of traditional dairy products around the globe.