In recent years ingredients market in India is witnessing an explosive growth, which was never seen earlier. As consumers are becoming more and more health conscious, the demand for more Functional foods that have reduced fat, no sugar added and are reduced in calories is likely to increase.
With the advancement in functional ingredients e.g., emulsifier/ stabilizers blends, Pro-biotic cultures, sugar and fat replaces, masking flavors, etc., it is now possible to manufacture dairy products, which are sugar-free, low calorie, low fat and have specific health benefit without compromising the taste & texture.
Thanks to the innovation in technology, distribution, communication coupled with positive demographic changes leading to the new product development and launches in the market, which are seen by many
consumers as a way to provide general health and well-being.
These dairy products are often referred as functional foods as they provide specific health benefits using our knowledge of nutrition & health relationship.
Why Need the Functional Foods..??
Alarming Increase in Obesity
According to FAO/WHO release 1.2 billion people are overweight and app 250 Million people are obese. World over overweight is a bigger problem than under-nourishment.

Diabetics
Word wide 177 million or 5.2 % of adult population are affected. The majority of this population is in Asia. Type 2 or non –insulin dependent diabetes mellitus account for 95 % of all cases, which can be, managed through diet modifications especially the type of carbohydrates.
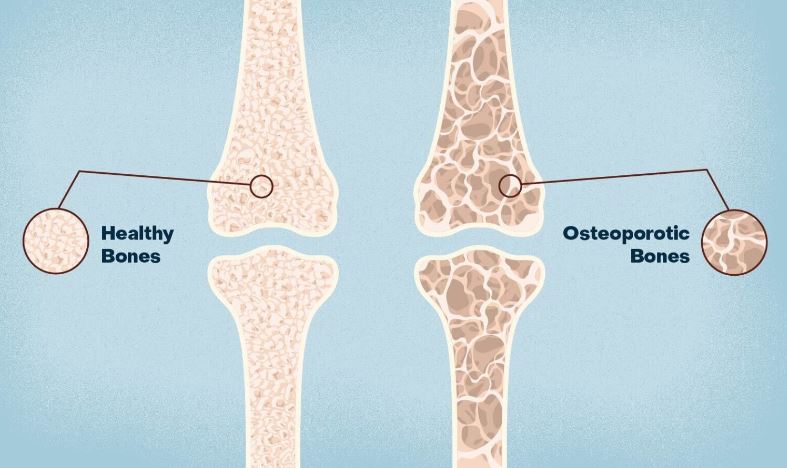
Osteoporosis
As per the WHO study the lifetime risk for Osteoporosis for women is between 30 and 40%. Calcium, Vitamin D and exercise are essential for prevention of Osteoporosis.
Health benefits and claims such as “calcium leads to bone health” are associated with dairy products
and are easily recognized by the consumers.
Healthy Foods Sales is Likely to Increase
There is an increasing consumer awareness of relationship between diet and health. Further, the customers are willing to pay extra for foods that can give some health benefits.
Consumer Demand for Low Calories Foods/ functional foods
Low calorie, reduced calorie foods and diabetic foods are becoming increasingly popular in all segments of food industry. This is seen by the launch of many low calorie ice cream and milk variants.
The above factors are responsible for creation of new market segment with enormous opportunities, which can be encased by being creative and innovative. Health concerns have also created a boom in low fat, low calorie foods.
This has led to strong demand for flavourings, which effectively mask the taste of sweeteners and artificially recreate the mouth feel of fat. Greater product diversity and more consumer choice are expected to drive the growth in this health & functional food segment.
Sugar Replace
In order to produce dairy products, which are significantly low in calories, it is necessary to reduce or remove the sugar. Bulking agents are needed to replace the loss of dry solids from sugar and retain an acceptable texture.
To compensate for the lack of sweetness it is often necessary to apply an intensive sweetener. A number of bulking agents for use in ice- cream/frozen desserts are available e.g., Litesse® polydextrose (1 Kcal/g), Lactitol (2 Kcal/g) and Maltodextrin (4 Kcal/g) are available in the market.
The application of sugars with a high level of sweetness (e.g., fructose, which is approx. twice as sweet as normal sucrose) makes it possible to reduce the total sugar content.
For tooth friendly application, xylitol is a sweetener of choice. It has the same sweetness intensity as sucrose, providing a “clean” sweetness with no discernable aftertaste. Xylitol has a positive influence of oral health and it inhibits the growth of Streptococcus Mutansis, which is associated with tooth decay.
A daily intake of 3-5 gram Xylitol will positively reduce tooth decay, plaque growth and plaque acidogenicity. The frozen desserts, which have xylitol in their recipe, have the following advantages:
- Helps fight bad breath
- Tooth friendly. Inhibits plaque formation
- Reduces tooth decay
- Encourages demineralisation of the teeth
- Good for diabetes
Before developing recipes for low calorie dairy products it is important to understand the functionality of the bulking agents. Foods with Low Glycemic Index (GI) have been scientifically validated as a tool in the management of diabetes and weight reduction.
GI factor is a ranking of foods from 0 – 100 that tells us whether a food will raise blood sugar levels just a little, moderately or dramatically. Based on GI Factor foods are classified as:
- Low GI foods <55
- Intermediate GI foods 55 – 70
- High GI foods > 70
Low GI foods are particularly important in maintaining blood sugar levels and managing weight. The FAO/WHO study recommends the use of low GI diets in order to prevent diseases such as Coronary heart disease, Diabetes and obesity. Therefore, the low GI diets are claimed to be healthier and more satiating.
Fat Replacer
Several products with extender and /or fat replacer properties are now commercially available. These fat replacers create a creamy sensation and improve the melt down properties in frozen desserts.
The addition of fat replacers compensates for some of the functional properties lost when fat content is reduced. Litesse® polydextrose, Lactitol, Maltodextrin ,Inulin are often used as fat replacers.
Flavorings
Low calorie dairy products have a reduced fat and/or sugar content. Due to low fat content following problems may be encountered:
- More pronounced taste of individual ingredients
- No masking effect from the fat e.g., oxidised/bitter taste from the dry milk
- Cardboard notes from the gums
- Change is sugar/salt balance
- Pronounced change in Body, texture and mount feel.
To prevent and optimize these problems, it is important to balance the flavoring and avoid volatile top notes. The flavoring dosages can then be reduced by up to 50 %. In addition, body & mouth feel can be improved by adding flavorings such as milk, cream &butter.
Functional flavorings especially developed for low fat and low sugar dairy products are commercially available.
Pre- and Probiotic
This is the most promising category, which include products like Dahi, Yoghurt, Lassi, Buttermilk, etc, which is easily recognisable by the Indian consumer.
In addition, Ice cream and frozen desserts can be developed containing both probiotic bacteria and pre-biotic carbohydrates (e.g., Lactitol, Polydextrose, etc.). In contrast to probiotic, which are live microbial additions, a pre-biotic is a non-viable component of diet that reaches the colon in an intact form and is selectively fermented by colon bacteria.
The studies have indicated that the viability of probiotic bacteria in ice cream changed little over a one-year period.
Addition of Different Bio-Actives
A number of whey, casein and dairy protein derived peptides and hydrolysates which act as a bio active peptides are already commercially available. These bioactive peptides can be used to position the products as anti-hypertensive, regulation of fat metabolism, etc. Ice cream and frozen desserts can also be used as vehicles to deliver bioactive dairy peptides.
Vitamin and Calcium Fortification
Many Dairy Products can be most readily adapted to nutrient fortification and inclusion of nutraceuticals.
Vitamin & calcium fortification is often carried out in infant foods & dairy products targeting women. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids can also be incorporated in the fat phase of the dairy products to provide functional benefits.
Therefore, many dairy products can be used successfully to deliver unique nutritional benefits to consumers beyond the basic
nutrition of current products.
Fiber-Enrichment
Inadequate intake of dietary fibre in the human diet has been implicated in many diseases e.g., constipation, obesity, diabetes, gallstones, lipid metabolism, appendicitis, etc.

Polydextrose is a good choice as an economical fiber source for use in ice cream and frozen desserts. Polydextrose is not digested in the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract and is partially fermented in the lower GI tract, making it a beneficial ingredient for digestive health.
The physiological benefits of polydextrose include increased fecal bulk, reduced transit time, lower fecal pH and reduced concentration of putrefactive substances in the colon.
Polydextrose’s prebiotic effects help promote growth of beneficial intestinal bacteria, while fermentation in the large intestine yields short-chain fatty acids, including butyrate. Improved GI function has been demonstrated with a daily intake of 4-12g of polydextrose without adverse effects.
In addition to the health benefits, polydextrose has multiple functional benefits in ice cream & frozen desserts. The freezing point depression factor is 0.6 vs. sucrose at 1.0; therefore, it can protect the structure of ice cream as it inhibits sugar recrystallization and
starch retrogradation.
It also improves storage stability by narrowing the difference between the storage temperature and the composite glass transition temperature of maximally frozen concentrated solutions for frozen desserts (Tg’).
The relative sweetness of polydextrose is practically zero so the sweetness of the finished product can be adjusted by using high-
intensity sweeteners.
Fortification can be as simple as adding protein, vitamins, minerals or complex carbohydrate. It can be a bit more complex through the addition of a variety of biologically active “nutraceutical” compounds.
Regulatory Issues
In light of the heath platform for dairy products it is pertinent to examine the current regulatory scenario in India. Food labelling is the primary means of communication between the producer and seller of food on one hand, and the purchaser and consumer on the other.
Brand loyalties are also attributed to the fact that label provides manufacturer’s guarantee on food safety & quality. Consumers have started understanding that food contain nutrients which if deficient can cause deficiency diseases or medical affliction.
The food labels help the consumer to choose right food. Indian consumer is now exposed to variety of food products not only from India but from across the border also due to globalization of food trade.
In order to communicate the health benefits of two types of claims can be used.
- Nutritional claim
- Health claims.
Nutritional claim refer to the composition of the food and do not inform the consumer directly about the effect the food may have on the body.
Health claims, on the other hand, inform the consumers about the beneficial effect the food has on the body.
The health claims connected to functional foods are either type A health claims that they enhance body functions or type B claims that they reduce the risk of disease.
Consumers in India often compare the label of imported food which gives enormous amount of information varying from Nutritional labelling to Health and Functional claims with that of similar food products which are available on the shelves of supermarkets. a
In the framework of Codex, matters relating to nutrition are of competence of the Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary uses (CCNFSDU) while Codex Committee on Food labelling has elaborated general standard of labelling of pre-packaged food and guidelines on claims and nutritional labelling.
Harmonisation of food labelling provisions with those of Codex is the need of the hour. Many developed and developing countries have
already harmonised their food labelling legislations with those of Codex. This has benefited the consumer and producer alike in these countries by way of new and innovative products being available in the market.
Further it will also ensure that the Claims made on the labels are based on sound scientific consensus and are not misleading to the consumer.
The multiplicity of laws and regulations in food sector need to be avoided. Therefore concerted efforts are needed on part of each agency involved in aligning Indian Food Standards with international standards.
Conclusion
Consumers are becoming more and more health conscious. As a result of this, the demand for more indulgent foods that have reduced fat, no sugar added and are reduced in calories is likely to increase.
Therefore, functional dairy products should address the widespread health issues to have significant consumer appeal. In order to be successful, the functional dairy products should give tangible benefits to the consumers which are supported by documented sound scientific investigations and associated claims must be sensible and credible.

